The Trust Wallet hack in December 2025 wasn’t just a headline for individual crypto users—it also served as a warning for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) that rely on cryptocurrency in their operations.
Though the attack primarily targeted personal wallets, the mechanics reveal vulnerabilities that affect crypto-friendly businesses, from fintech startups to decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
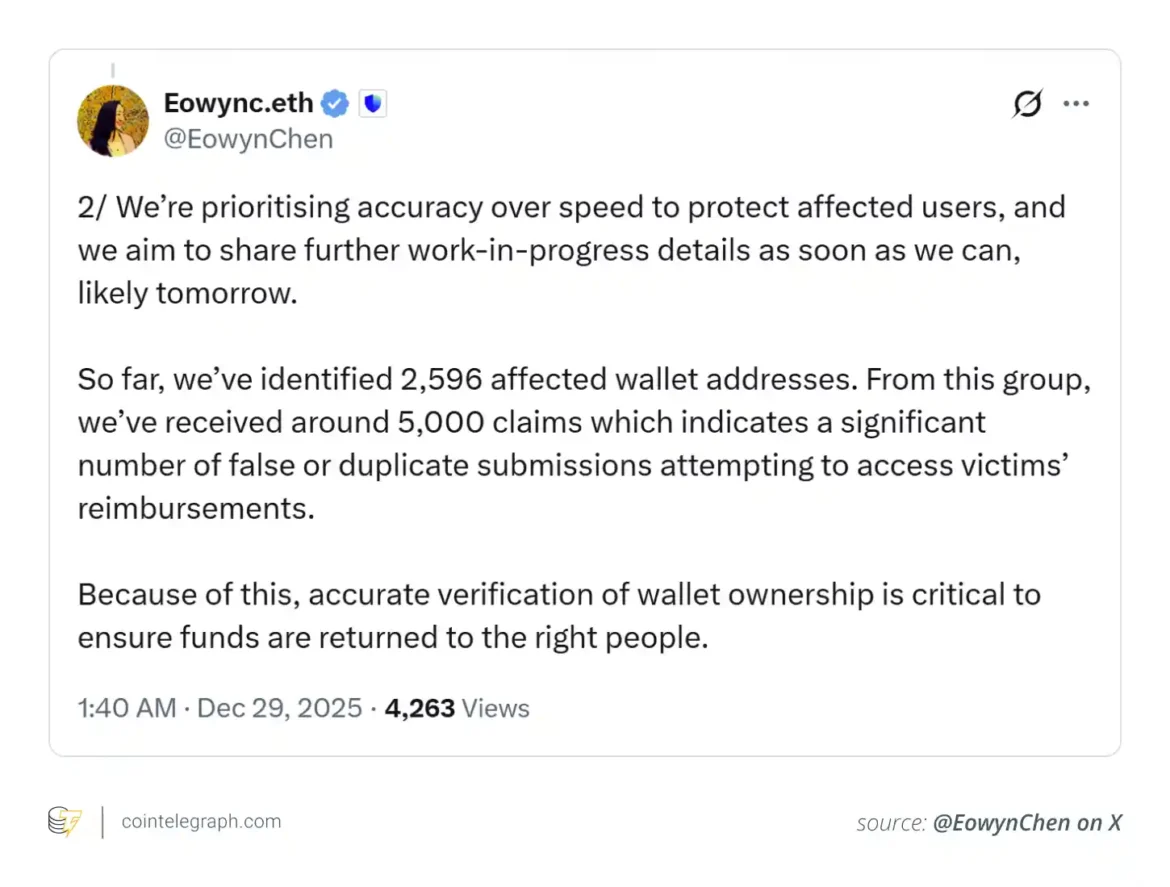
The breach resulted in roughly $7 million in stolen assets and sparked a wave of questions about wallet security, supply-chain risks, and the resilience of verification processes.
For SMEs, it’s a case study in how convenience can sometimes be the enemy of safety.
What Happened During the Hack
Between December 24 and 26, 2025, attackers exploited Trust Wallet’s Chrome browser extension with a malicious update affecting version 2.68.
This allowed them to steal funds from 2,596 verified wallets, with nearly 5,000 reimbursement claims filed afterward.
The attack was sophisticated. Security experts found that malicious JavaScript had been inserted into the extension, enabling the theft of private keys and recovery phrases during normal wallet usage.
It’s likely the perpetrators used a stolen Chrome Web Store API key, letting them distribute the update through official channels instead of relying on phishing attempts.
Once the keys were compromised, stolen funds moved quickly through exchanges and cross-chain bridges, making recovery extremely difficult.
Trust Wallet responded by disabling the affected extension version, releasing a patch (version 2.69), and establishing a verification process for claims.
Key takeaway: Even trusted software update mechanisms can fail, and hot wallets remain highly exposed to supply-chain attacks.
Impact on the Crypto Community
The hack rattled confidence in browser-based wallets.
Many users were unaware that such wallets function as hot wallets, exposing them to malware and malicious updates despite their ease of use.
Beyond Trust Wallet, the attack reignited debates about self-custody.
Hardware wallets and offline storage were again highlighted as safer alternatives, particularly for larger holdings.
For SMEs, the incident underscores how risks extend beyond internal systems.
Browser extensions, APIs, and third-party libraries are widely used in payroll, treasury management, and other crypto-facing operations—meaning vulnerabilities in external tools can have real financial consequences.
Verification Challenges and Claims Processing
Handling reimbursements turned out to be more complicated than expected.
With almost 5,000 claims for roughly 2,500 affected wallets, the process risked being overwhelmed by duplicates or fraudulent submissions.
Trust Wallet required detailed verification, including wallet addresses, transaction histories, and attacker addresses.
This created operational strain and delayed legitimate refunds.
For SMEs, this is a clear lesson: verification processes must be planned ahead of time.
A well-defined framework for identity, access, and transaction checks can prevent bottlenecks and preserve trust during crises.
Common Vulnerabilities for Crypto-Using SMEs
The Trust Wallet hack highlights vulnerabilities that aren’t unique to large exchanges or individual wallets. SMEs face similar risks:
1. Supply-chain and update risks
Relying on browser extensions, SDKs, APIs, or cloud services increases attack surfaces. Any compromised component can lead to rapid financial losses.
2. Overreliance on hot wallets
Hot wallets are convenient but vulnerable to malware, malicious updates, and private-key theft. SMEs should weigh convenience against exposure.
3. Social engineering and phishing
Post-incident periods see a spike in phishing and impersonation attempts, targeting users during a moment of uncertainty. Staff training is essential to reduce risk.
Security Measures SMEs Can Take
The Trust Wallet incident offers several actionable lessons:
-
Cold storage for major assets: Keep most cryptocurrency offline to limit exposure. Hot wallets should only hold funds needed for day-to-day use.
-
Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Enforce MFA across wallets, approvals, and controls.
-
Incident response planning: Prepare and rehearse emergency procedures for attacks, including containment, reporting, and recovery.
-
External audits: Independent security reviews can uncover gaps internal teams may overlook.
-
Access controls and supplier monitoring: Limit who can access wallets, whitelist addresses, and assess third-party security practices.
-
Staff and user education: Train employees and users to recognize phishing attempts and impersonation scams.
Regulatory Considerations
While no immediate regulations followed the Trust Wallet hack, global scrutiny of the crypto sector is increasing.
SMEs face growing expectations around custody, reporting, and consumer protection.
Security failures can now carry not only financial and reputational consequences but also potential compliance risks.
Staying proactive with technical and procedural safeguards is becoming as important as day-to-day business operations.
Takeaways for SMEs
The December 2025 Trust Wallet hack was a stark reminder that convenience can come at a cost.
Supply-chain vulnerabilities, reliance on hot wallets, and unprepared verification processes all played a role in magnifying losses.
For SMEs navigating the crypto space, the incident underscores the importance of:
-
Planning verification and reimbursement frameworks before incidents occur
-
Reducing hot wallet exposure
-
Implementing strong access controls, security audits, and employee training
-
Staying aligned with evolving regulatory expectations
By learning from high-profile breaches like this one, SMEs can better protect their crypto assets and maintain trust with clients and stakeholders.
Share on Facebook «||» Share on Twitter «||» Share on Reddit «||» Share on LinkedIn